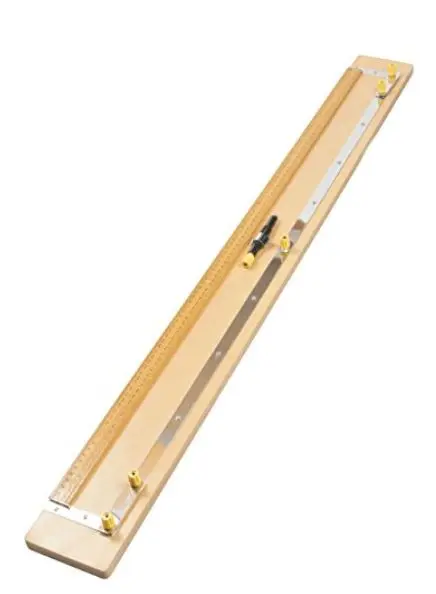
A metre bridge is a precision electrical instrument used in physics and electrical laboratories to determine the unknown resistance of a conductor using the principles of a Wheatstone bridge. It consists of a uniform metallic wire, typically 1 meter in length, mounted on a calibrated wooden or metallic base with a scale marked in centimeters.
Key Features:
- Bridge Wire: A high-resistance alloy wire (usually nichrome or constantan) of uniform cross-section and exactly 1 meter in length ensures accurate measurements.
- Scale and Base: Mounted on a rigid, insulating base with a clearly marked metric scale (0–100 cm) for precise length measurements.
- Terminals: Four brass terminals or binding posts allow for secure connections to the known resistance, unknown resistance, galvanometer, and battery.
- Galvanometer Jockey: Used in conjunction with a jockey and a galvanometer to detect the null point (zero deflection), which indicates a balanced bridge condition.
Applications:
- Accurate measurement of unknown resistances.
- Verification of the principle of the Wheatstone bridge.
- Study of resistivity and conductivity of different materials.
- Educational tool in physics experiments related to electrical circuits and Ohm’s Law.
The metre bridge is an essential component in physics education and electrical measurement experiments, valued for its simplicity, reliability, and precision in resistance determination.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.