Ammeter
Description:
-
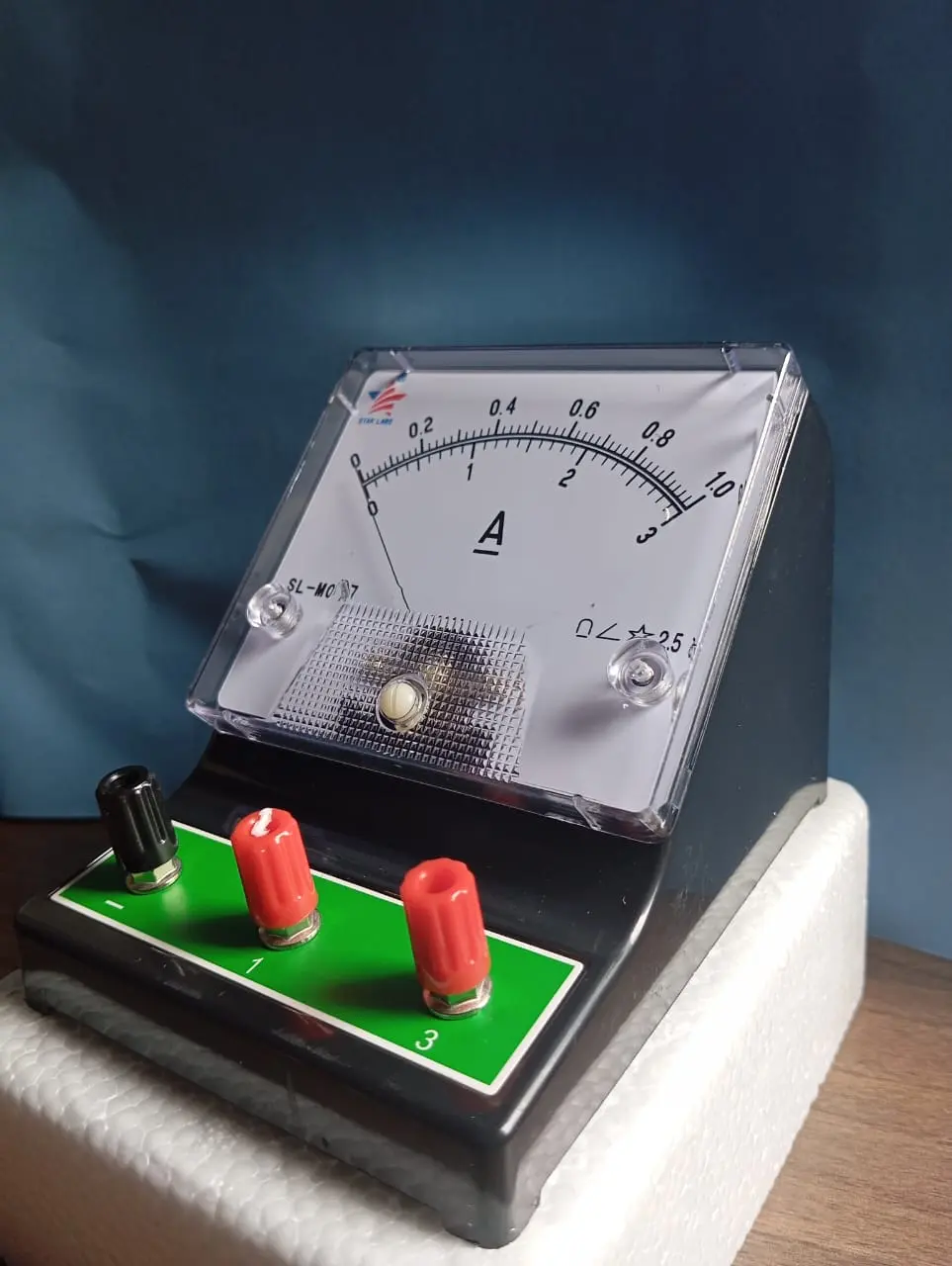
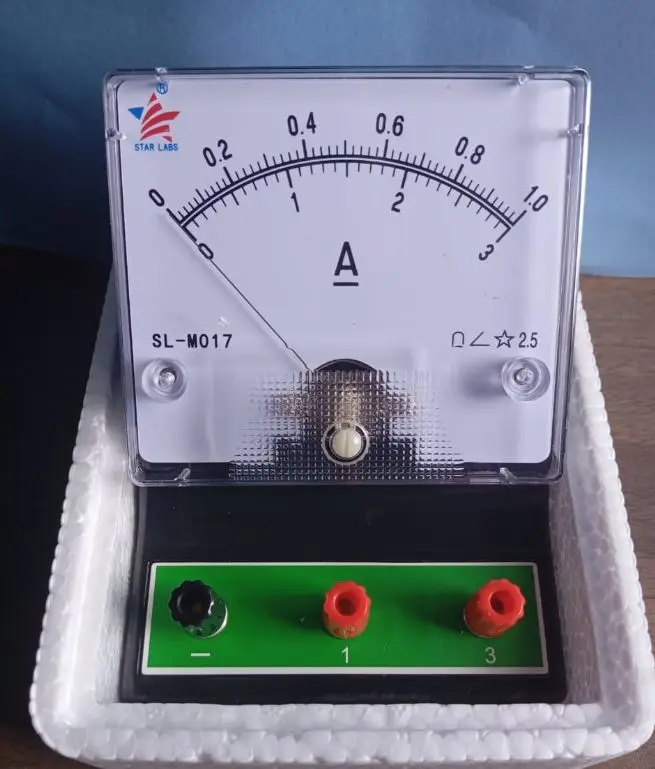
Structure: An analog ammeter typically consists of a circular or semi-circular dial with graduations (scale markings) for current readings, and a needle that moves along the scale in response to the current flowing through the circuit.
-
Needle Movement: The needle moves in response to the magnetic field generated by the current flowing through the ammeter’s internal coil. The amount of deflection indicates the strength of the current.
-
Scale: The scale on the meter is usually graduated in amperes (A), and the dial may have multiple ranges for different current levels (e.g., 0-1 A, 0-10 A, etc.). The user can switch between these ranges to measure small or large currents.
-
Internal Coil: Analog ammeters often use a moving coil meter design. The coil is placed in a magnetic field, and as current flows through it, it experiences a force that causes the needle to move.
Function:
-
Current Measurement: The main function of the analog ammeter is to measure electric current (usually in amperes), which is crucial in testing and troubleshooting electrical circuits.
-
Visual Indication: The ammeter provides a continuous and real-time visual representation of the current flowing through a circuit. The movement of the needle directly correlates to the amount of current.
-
Range Selection: Some analog ammeters have a range selector switch that allows users to choose different scales for measuring higher or lower currents, ensuring the device can measure a wide range of current values.
Key Features:
-
Analog Display: Unlike digital ammeters, which provide numerical readings, analog ammeters display the measurement on a dial with a needle, offering a visual, continuous reading that can be more intuitive for some users.
-
Multiple Ranges: Analog ammeters typically feature different range settings (e.g., milliampere, ampere) to measure both low and high currents accurately.
-
Durability: Analog ammeters are relatively rugged and often more durable in harsh environments compared to digital meters, which can be more sensitive to damage from impacts or moisture.
Common Uses:
-
Current Measurement in Circuits: Analog ammeters are used to measure the current in electrical circuits for testing and troubleshooting purposes. They can be used in both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) circuits.
-
Testing Electrical Devices: They are used to check whether electrical devices or components (such as resistors, batteries, or power supplies) are operating within their rated current levels.
-
Educational and Laboratory Settings: Analog ammeters are commonly used in schools and laboratories for teaching electrical principles and for experiments involving current measurement.
-
Automotive and Industrial Applications: Analog ammeters can be found in automotive electrical systems to measure current draw from batteries or alternators. They are also used in industrial equipment to monitor and control electrical currents.